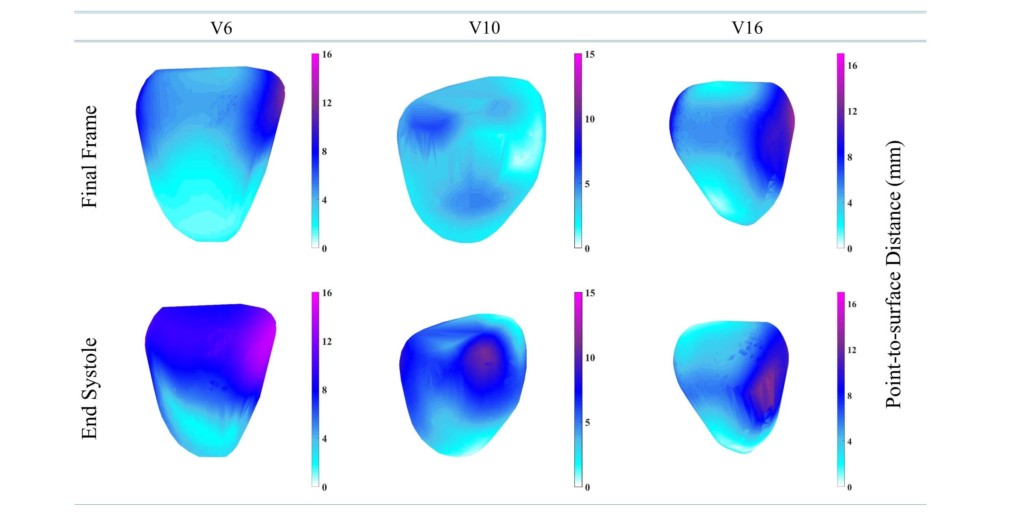
Scientists from the Warwick Manufacturing Group (University of Warwick, Warwick, UK) have developed a new 3D MRI computing technique that involves a numerically stable technique of left ventricle myocardial tracking, a 3D extension of local weighted mean function to transform MRI pixels, and a 3D extension of Hierarchical Template Matching model for myocardial tracking problems.
According to a press release, the new technique is less stressful for the patient and carried out in less time. 3D MRI computing can measure strain in the heart using image registration method. Traditionally, when a patient goes for an MRI scan they are given a dose of gadolinium, which reacts the magnetic field of the scanner to produce an image of the protons in the metal realigning with the magnetic field. The faster the protons realign, the brighter the image features and can show where the dead muscles are in the heart and what the diagnosis is. The dose of gadolinium can have detrimental effects to other parts of the body, particularly the risk of kidney failure.
Mark Williams, from WMG at the University of Warwick, says: “Using 3D MRI computing technique we can see in more depth what is happening to the heart, more precisely to each heart muscles, and diagnose any issues such as remodelling of heart that causes heart failure. The new method avoids the risk of damaging the kidney opposite to what traditional methods do by using gadolinium.”
Jayendra Bhalodiya, who conducted the research from WMG, University of Warwick adds: “This new MRI technique also takes away stress from the patient, as during an MRI the patient must be very still in a very enclosed environment meaning some people suffer from claustrophobia and have to stop the scan, often when they do this they have to administer another dose of the damaging gadolinium and start again. This technique doesn’t require a dosage of anything, as it tracks the heart naturally.”
A report of the 3D MRI computing technique, titled “hierarchical template matching for 3D myocardial tracking and cardiac strain estimation”, has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.