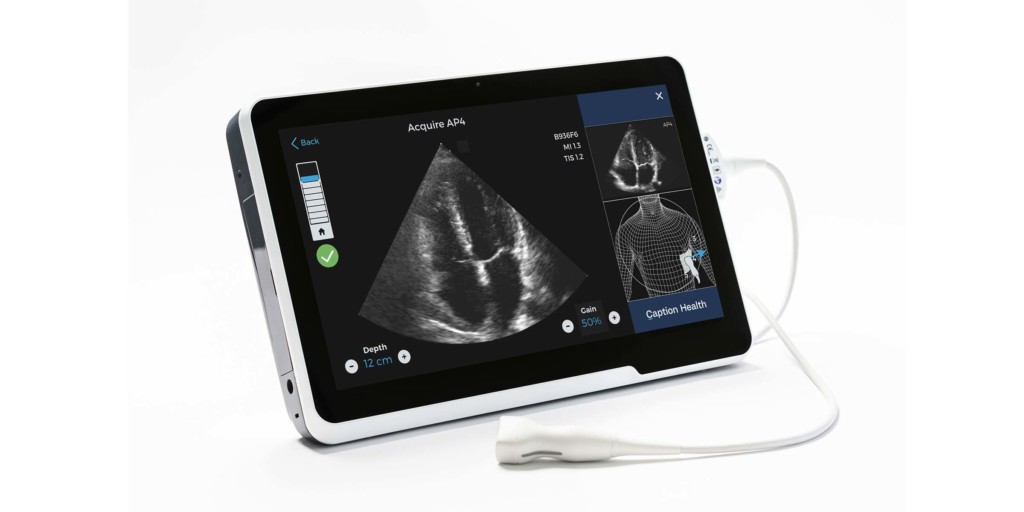
Caption guidance
Caption Health has announced that the FDA has authorised marketing of Caption Guidance software, which is designed to assist medical professionals in the acquisition of cardiac ultrasound images. The system uses artificial intelligence (AI) to provide real-time guidance and diagnostic quality assessment of images. The aim is to empower healthcare providers—even those without prior ultrasound experience—with the ability to capture diagnostic quality images. A press release states that empowering more clinicians with ultrasound image acquisition capability will bring the benefits of ultrasound to more patients, help standardise the quality of care, and help institutions realise valuable cost and time savings.
Caption Guidance was authorised via the de novo pathway, which is a regulatory pathway reserved for novel technologies. According to the press release, the granting of this de novo is ground-breaking because Caption Guidance is the first medical software authorised by the FDA that provides real-time AI guidance for medical imaging acquisition. Caption Guidance is equipped with numerous features that together act as a co-pilot for clinicians when performing an ultrasound exam. The software emulates the guidance that an expert sonographer would provide to optimise the image, including providing real-time guidance on how to manipulate the transducer, and automated feedback on diagnostic image quality.
Marketing authorisation was granted after the FDA reviewed extensive performance testing, including data from a pivotal multicentre prospective clinical trial conducted by Northwestern Medicine and Minneapolis Heart Institute at Allina Health, evaluating the use of Caption Guidance by registered nurses with no prior ultrasound experience.
In this study, eight registered nurses with no prior ultrasound experience used Caption Guidance to perform ultrasound exams on 240 patients, following a short training course. Patients were stratified to include a wide range of body-mass index and cardiac pathologies. The nurses acquired limited echo exams of 10 views each. Each exam was assessed by a panel of five expert cardiologists to determine if the exam was of sufficient quality to make a set of specific qualitative visual assessments.
Caption Guidance successfully met all four primary endpoints, meeting the prespecified criteria for study success by acquiring images of sufficient quality for specific clinical assessments. Namely, the nurses successfully acquired limited echo exams for qualitative visual assessments of left ventricular size: 98.8%, 95% CI [96.7, 100]; left ventricular function: 98.8% [96.7, 100]; right ventricular size: 92.5% [88.1, 96.9]; and pericardial effusion: 98.8% [96.7, 100].
John Bailitz (Northwestern Medicine, Minneapolis, USA), states: “Point-of-care ultrasound has been demonstrated to expedite time to diagnosis, reduce the need for costlier testing, and decrease complications from invasive procedures. Caption Guidance can unlock these benefits by addressing one of the largest barriers to ultrasound adoption: the ability to acquire diagnostic quality images quickly.”
Andy Page, CEO of Caption Health, comments: “No patient should have to forgo a potentially life-saving cardiac ultrasound. Through the power of AI, Caption Guidance will provide patients with unprecedented access to ultrasound when and where they need it most.”